What Forces May Have Caused Various Changes In The Caminalcules Population Over Time
What is Darwin's Theory of Evolution?

The Theory of Evolution by natural selection was get-go formulated in Charles Darwin's book "On the Origin of Species" published in 1859. In his book, Darwin describes how organisms evolve over generations through the inheritance of physical or behavioral traits, as National Geographic explains. The theory starts with the premise that inside a population, there is variation in traits, such every bit beak shape in one of the Galapagos finches Darwin studied.
According to the theory, individuals with traits that enable them to adapt to their environments will help them survive and take more offspring, which will inherit those traits. Individuals with less adaptive traits volition less frequently survive to laissez passer them on. Over time, the traits that enable species to survive and reproduce will become more frequent in the population and the population volition change, or evolve, according to BioMed Central. Through natural selection, Darwin suggested, genetically diverse species could arise from a common ancestor.
Darwin did not know the mechanism past which traits were passed on, according to National Geographic. He did non know about genetics, the machinery by which genes encode for certain traits and those traits are passed from one generation to the side by side. He likewise did not know nearly genetic mutation, which is the source of natural variation. Simply future research by geneticists provided the mechanism and additional evidence for evolution by natural pick
What is natural selection?
Darwin chose the term "natural option" to be in dissimilarity with "artificial selection," in which creature breeders select for item traits that they deem desirable. In natural selection, it'due south the natural environment, rather than a homo beingness, that does the selecting.
Put simply, the theory of development by means of natural pick can exist described equally "descent with modification," said Briana Pobiner, an anthropologist and educator at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History in Washington, D.C., who specializes in the report of human origins. The theory is sometimes described as "survival of the fittest," just that characterization tin can be misleading, Pobiner said. Here, "fitness" refers not to an organism'due south force or athleticism but rather its power to survive and reproduce.
Natural selection can alter a species in small ways, causing a population to modify color or size over the form of several generations, co-ordinate to The Natural History Museum. When this process happens over a relatively short period of time and in a species or small-scale group of organisms, scientists telephone call it "microevolution."
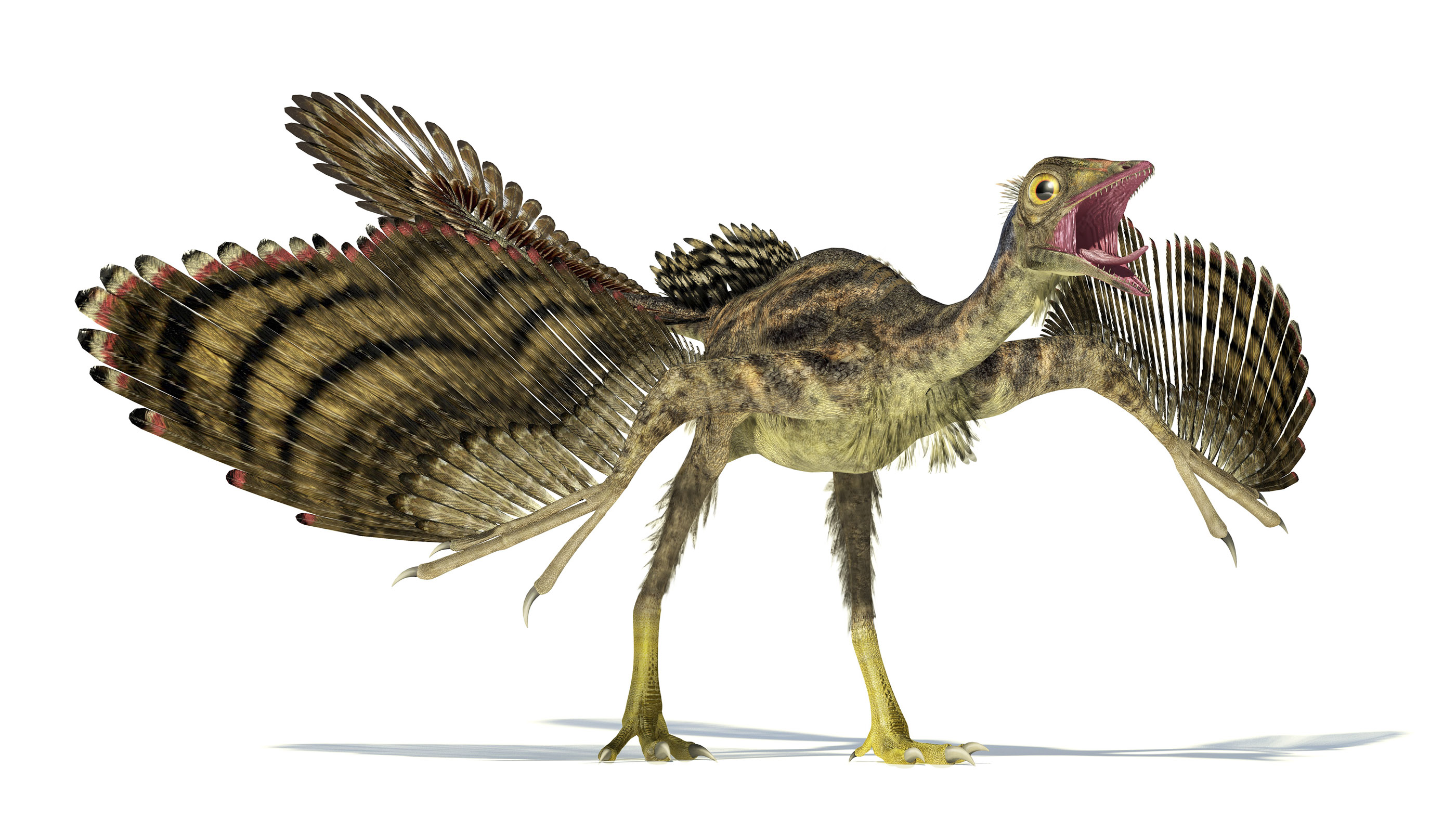

Merely when given enough fourth dimension and accumulated changes, natural choice tin can create entirely new species, a procedure known every bit "macroevolution," according to Derek Turner and Joyce C. havstad in "The Philosophy of Macroevolution." This long-term process is what turned dinosaurs into birds, amphibious mammals (such as an animate being called Indohyus) into whales and a mutual antecedent of apes and humans into the people, chimps and gorillas we know today.
Darwin also described a form of natural option that depends on an organism'southward success at attracting a mate — a procedure known as sexual selection, co-ordinate to Nature Instruction. The colorful plume of peacocks and the antlers of male deer are both examples of traits that evolved under this type of selection.
How did whales evolve?
One of the best examples scientists take of natural selection, is the evolution of whales. Past using Darwin's theory as a guide, and understanding how natural choice works, biologists determined that the transition of early on whales from state to water occurred in a series of predictable steps.
The evolution of the blowhole, for example, might have started with random genetic changes that resulted in at to the lowest degree one whale having its nostrils further dorsum on its head, according to Phys.org.
The whales with this adaptation would have been improve suited to a marine lifestyle, since they would not accept had to completely surface to breathe. Such individuals were more successful and had more offspring. In after generations, more genetic changes occurred, moving the nose farther dorsum on the caput.
Other body parts of early whales also changed. Front legs became flippers. Back legs disappeared. Their bodies became more than streamlined, and they developed tail flukes to ameliorate propel themselves through water, according to the Natural History Museum.
Even though scientists could predict what early whales should look similar, for a long fourth dimension they lacked the fossil evidence to back up their claim. Creationists viewed this absence, not but with regard to whale development but more generally, as proof that evolution didn't occur, as pointed out in a Scientific American commodity.
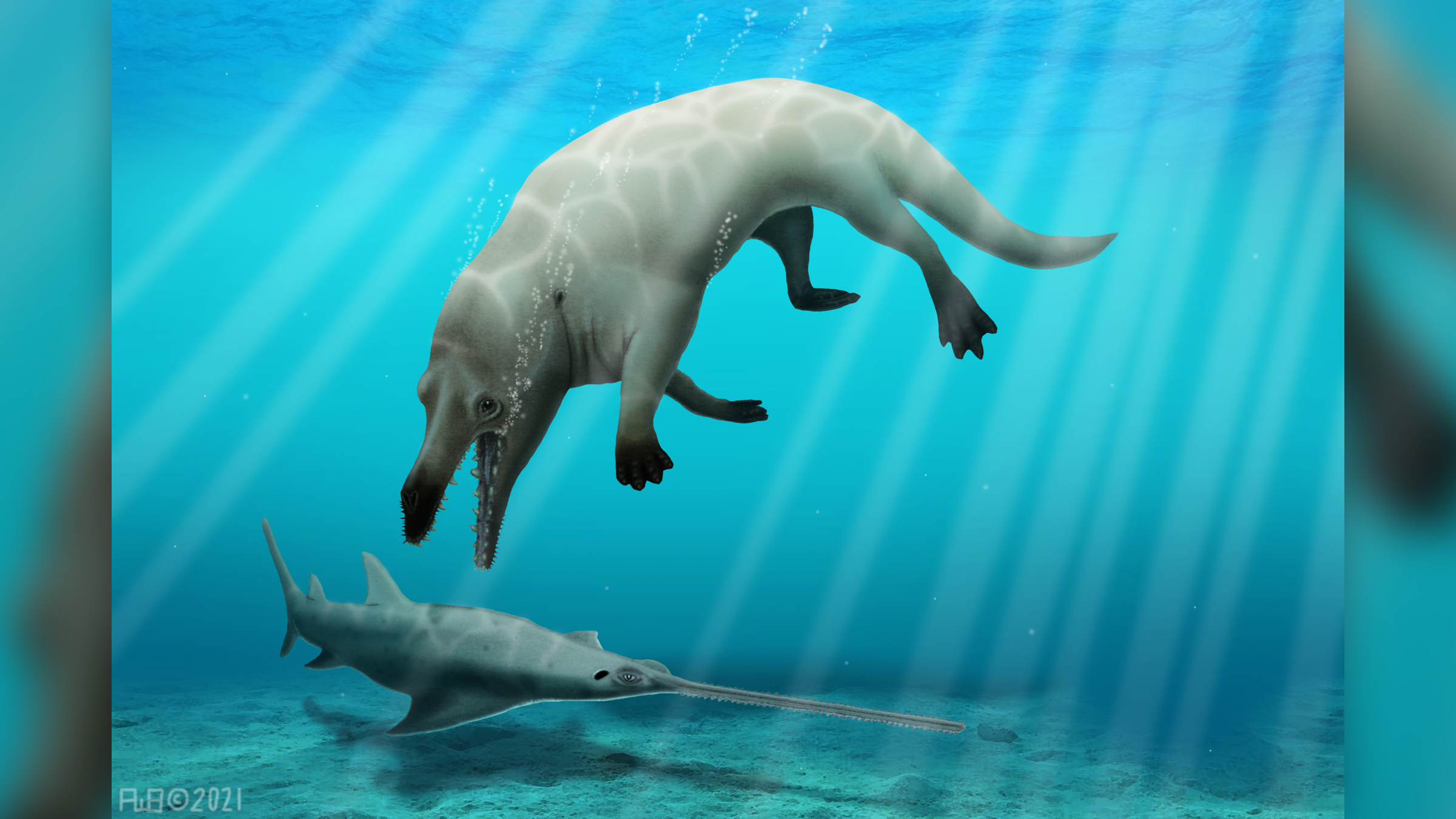

Nevertheless, since the early 1990s, scientists have institute evidence from paleontology, developmental biological science and genetics to support the idea that whales evolved from state mammals. These same lines of evidence support the theory of evolution as a whole.
In the first edition of "On the Origin of Species," Darwin speculated nigh how natural selection could crusade a land mammal to turn into a whale. Every bit a hypothetical case, Darwin used Due north American black bears (Ursus americanus), which were known to catch insects by swimming in the h2o with their mouths open, according to the Darwin Correspondence Project.
"I can meet no difficulty in a race of bears being rendered, by natural selection, more aquatic in their structure and habits, with larger and larger mouths, till a creature was produced as monstrous every bit a whale," he speculated.
The thought didn't go over very well with the public or with other scientists. Darwin was so embarrassed by the ridicule he received that the swimming-bear passage was removed from later editions of the book. Scientists now know that Darwin had the right idea but the wrong animal. Instead of looking at bears, he should have been looking at cows and hippopotamuses.
Other theories of evolution
Darwin wasn't the first or but scientist to develop a theory of development. Around the same time as Darwin, British biologist Alfred Russel Wallace independently came upwardly with the theory of evolution past natural option, according to the Natural History Museum. However this had little impact.
"The concept of development every bit a historical event was a hot topic among biologists and geologists prior to Darwin'due south book because there was so much evidence accumulating, just I suspect biological evolution hadn't actually impinged on people outside of the bookish bunker," Dr. P John D. Lambshead, a retired science research leader in marine biodiversity, ecology, and evolution at The Natural History Museum, London, told All Almost History Mag. "As long as science knew of no mechanism to explain how evolution happened it could be safely dismissed as a crank idea."
Meanwhile, French biologist Jean-Baptiste Lamarck proposed that an organism could pass on traits to its offspring, though he was wrong about some of the details, co-ordinate to the Academy of California'southward Museum of Paleontology.
Like Darwin, Lamarck believed that organisms adapted to their environments and passed on those adaptations. He idea organisms did this by irresolute their behavior and, therefore, their bodies — like an athlete working out and getting vitrify — and that those changes were passed on to offspring.
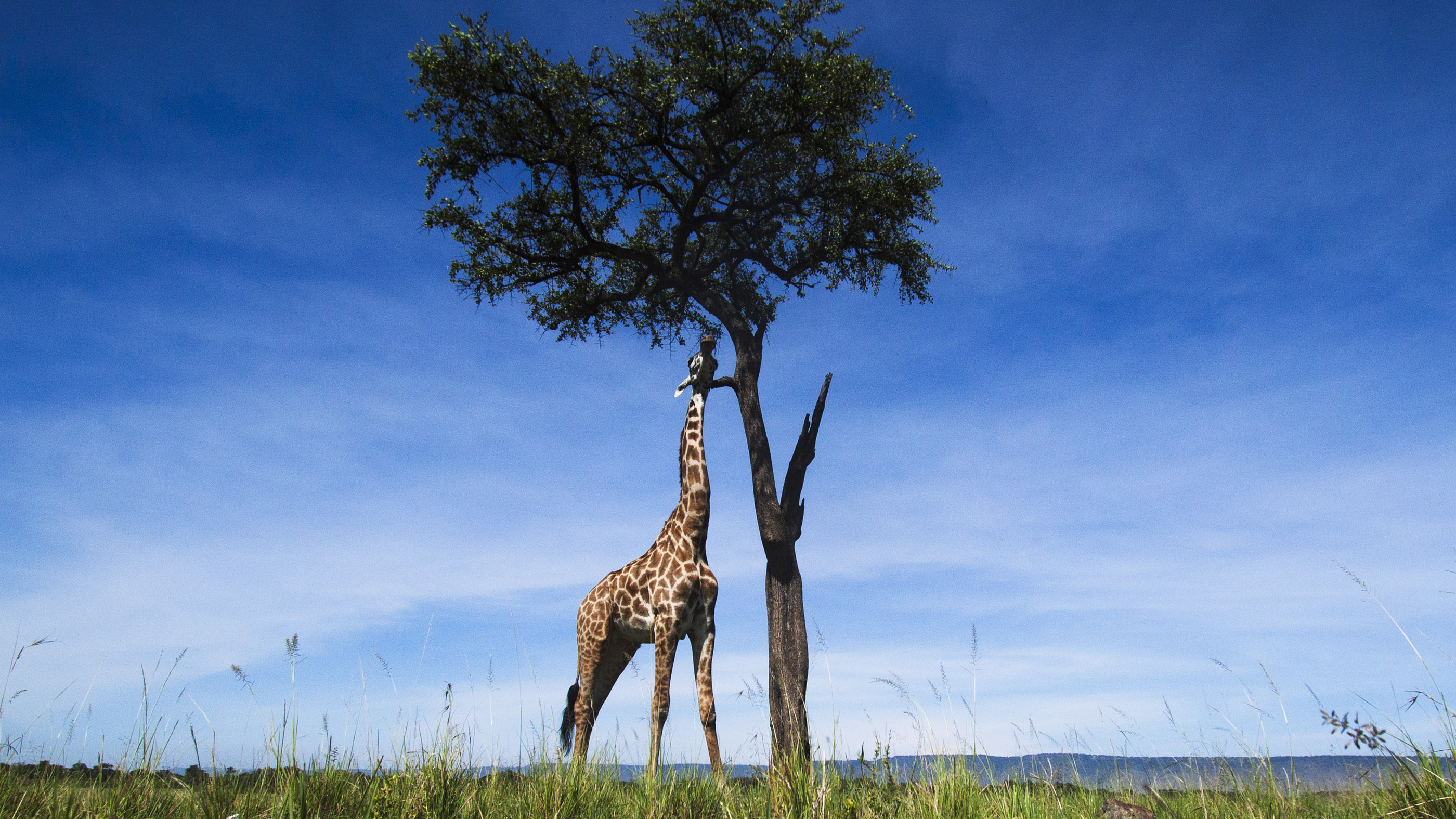

For example, Lamarck thought that giraffes originally had shorter necks only that, as trees effectually them grew taller, they stretched their necks to reach the tasty leaves and their offspring gradually evolved longer and longer necks. Lamarck as well believed that life was somehow driven to evolve through the generations from simple to more complex forms, according to Understanding Evolution, an educational resource from the University of California Museum of Paleontology.
Though Darwin wasn't sure of the machinery past which traits were passed on, he did not believe that evolution necessarily moved toward greater complication, co-ordinate to Understanding Evolution — rather, he believed that complication arose through natural choice.
A Darwinian view of giraffe development, co-ordinate to Quanta Magazine, would exist that giraffes had natural variation in their neck lengths, and that those with longer necks were meliorate able to survive and reproduce in environments total of tall trees, and then that subsequent generations had more and more long-necked giraffes.
The main deviation between the Lamarckian and Darwinian ideas of giraffe evolution is that there'south nothing in the Darwinian explanation about giraffes stretching their necks and passing on an acquired characteristic.
What is mod evolutionary synthesis?
According to Pobiner, Darwin did non know anything almost genetics. "He observed the pattern of evolution, only he didn't really know about the mechanism," she said. That came after, with the discovery of how genes encode different biological or behavioral traits, and how genes are passed down from parents to offspring. The incorporation of genetics into Darwin's theory is known every bit "modern evolutionary synthesis."
The concrete and behavioral changes that make natural selection possible happen at the level of DNA and genes within the gametes, the sperm or egg cells through which parents pass on genetic material to their offspring. Such changes are chosen mutations. "Mutations are basically the raw fabric on which evolution acts," Pobiner said.
Mutations can be caused past random errors in DNA replication or repair, or by chemical or radiations damage, according to Nature Instruction. Usually, mutations are either harmful or neutral, only in rare instances, a mutation might testify benign to the organism. If and so, information technology volition go more prevalent in the next generation and spread throughout the population.
In this fashion, natural pick guides the evolutionary process, preserving and calculation upward the benign mutations and rejecting the bad ones. "Mutations are random, but selection for them is not random," Pobiner said.
But natural selection isn't the only mechanism by which organisms evolve, she said. For example, genes can be transferred from one population to another when organisms drift or immigrate — a process known as cistron menstruum. And the frequency of certain genes tin also change at random, which is chosen genetic drift.
The reason Lamarck'southward theory of evolution is generally wrong is that acquired characteristics don't affect the Deoxyribonucleic acid of sperm and eggs. A giraffe'southward gametes, for example, aren't affected by whether it stretches its neck; they but reflect the genes the giraffe inherited from its parents. Only equally Quanta reported, some aspects of evolution are Lamarckian.
For instance, a Swedish study published in 2002 in the European Journal of Human Genetics found that the grandchildren of men who starved as children during a famine passed on amend cardiovascular health to their grandchildren. Researchers hypothesize that although experiences such as food deprivation don't change the DNA sequences in the gametes, they may effect in external modifications to DNA that turn genes "on" or "off."
Such changes, called epigenetic changes, do not modify the bodily Deoxyribonucleic acid sequence itself. For instance, a chemic modification called methylation tin affect which genes are turned on or off. Such epigenetic changes can exist passed downwardly to offspring. In this way, a person'southward experiences could affect the Deoxyribonucleic acid he or she passes downwards, coordinating to the way Lamarck idea a giraffe craning its neck would touch the neck length of its offspring.
What is the show for development?
The Theory of Evolution is one of the best-substantiated theories in the history of science. It is supported by evidence from a wide diverseness of scientific disciplines, including genetics, which shows that unlike species have similarities in their DNA.
There is also bear witness supporting the Theory of Evolution in paleontology and geology. This is through the fossil record, which shows how that species that existed in the by are different from those present today, according to Bruce S. Lieberman and Roger L. Kaesler in "Prehistoric Life: Development and the Fossil Record" (Wiley, 2010).
In that location is also evidence for Darwin's theory establish in developmental biology. Information technology has been discovered that species that seem very different as adults laissez passer through similar stages of embryological evolution, suggesting a shared evolutionary past, co-ordinate to the open-access textbook "Concepts of Biology."
Bear witness for whale evolution from paleontology
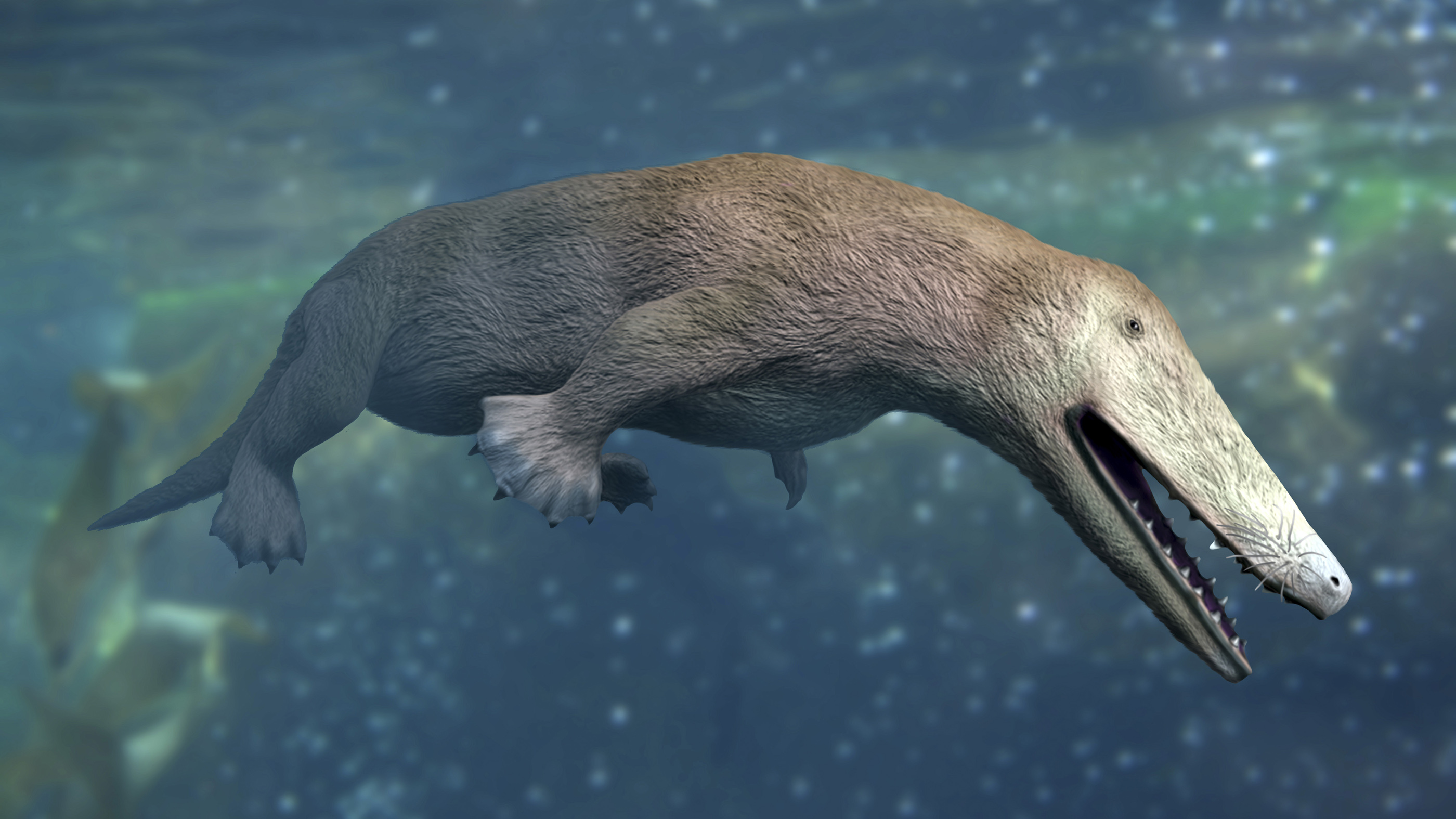

The disquisitional piece of evidence was discovered in 1994, when paleontologists found the fossilized remains of Ambulocetus natans, which means "swimming-walking whale," according to a 2009 review published in the periodical Evolution: Education and Outreach. Its forelimbs had fingers and pocket-size hooves, but its hind feet were enormous relative to its size. The creature was clearly adapted for pond, simply it was also capable of moving clumsily on land, much like a seal.
When information technology swam, the aboriginal fauna moved like an otter, pushing back with its hind feet and undulating its spine and tail.
Modernistic whales propel themselves through the water with powerful beats of their horizontal tail flukes, only A. natans still had a whip-similar tail and had to apply its legs to provide near of the propulsive force needed to motility through water.
In recent years, more than and more of these transitional species, or "missing links," take been discovered, lending farther support to Darwin'due south theory. For instance, in 2007, a geologist discovered the fossil of an extinct aquatic mammal, called Indohyus , that was about the size of a cat and had hooves and a long tail.
Scientists retrieve the animal belonged to a grouping related to cetaceans such every bit Ambulocetus natans. This beast is considered a "missing link" betwixt artiodactyls — a group of hoofed mammals (fifty-fifty-toed ungulates) that includes hippos, pigs, and cows — and whales, according to the National Science Foundation.
Researchers knew that whales were related to artiodactyls, but until the discovery of this fossil, there were no known artiodactyls that shared physical characteristics with whales. Afterward all, hippos, thought to be cetaceans' closest living relatives, are very dissimilar from whales. Indohyus, on the other hand, was an artiodactyl, indicated past the construction of its hooves and ankles, and it likewise had some similarities to whales, in the structure of its ears, for example.
Bear witness for whale evolution from genetics & developmental biology

Genetic testify also supports the idea that whales evolved from country mammals and provides information virtually the exact branching of the evolutionary tree. For instance, in 1999, researchers reported in the periodical Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences that according to genetic assay of "jumping cistron" sequences, which copy and paste themselves into genomes, hippos were whales' closest living relatives. Before 1985, researchers thought pigs were more closely related to whales, merely this 1999 study overturned that idea, every bit the Associated Press reported.
In 2019, researchers reported in the journal Science Advances about which genes within the whale genome were inactivated during the process of the creature'due south development from land mammals, equally Science Fri reported. The researchers could tell that certain genes, including one involved in making saliva, had been inactivated because there are remnants of them, which the researchers call genomic fossils, in whale genomes. This indicates that whales evolved from a salivating creature.
In that location'due south also testify of cetacean evolution from developmental biology. Developmental biology illustrates the fact that animals that are very different as adults share similarities as embryos because they are evolutionarily related. For instance, as embryos, cetaceans started to develop hind limbs, which disappear later in evolution, while the forelimbs remain and develop into flippers, according to the periodical Development: Education and Outreach. This suggests that cetaceans evolved from a iv-legged ancestor.
Is the theory of evolution controversial?
Despite the wealth of bear witness from the fossil record, genetics and other fields of science, some people yet question the theory of evolution'south validity. Some politicians and religious leaders denounce the theory, invoking a higher beingness as a designer to explicate the complex world of living things, particularly humans.
School boards fence whether the theory of development should be taught aslope other ideas, such as intelligent design or creationism.
Mainstream scientists see no controversy. "A lot of people have deep religious beliefs and also have evolution," Pobiner said, adding, "in that location can exist existent reconciliation."
Evolution is well supported by many examples of changes in diverse species leading to the diversity of life seen today. "Natural selection, or to put it some other way — variation, heredity, and differential fitness — is the cadre theory of modern biology," John Lambshead explains. "Information technology is to biology what, say quantum mechanics and special relativity are to physics or the atomic model is to chemical science."
Additional reporting by contributors Alina Bradford, Ashley P. Taylor and Callum McKelvie
Additional resources
- The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration has a presentation on whale evolution.
- To read the theory in its original grade, run across Darwin'southward volume, "On the Origin of Species."
- Check out this commodity for an overview of natural pick.
- To understand the difference between a theory and fact, see this National University of Sciences website.
Source: https://www.livescience.com/474-controversy-evolution-works.html
Posted by: hodgesdarm1977.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Forces May Have Caused Various Changes In The Caminalcules Population Over Time"
Post a Comment